coo_scale scales the coordinates by a 'scale' factor. If not provided,
assumed to be the centroid size. It involves three steps: centering from current position,
dividing coordinates by 'scale', pushing back to the original position.
coo_scalex applies a scaling (or shrinking) parallel to the x-axis,
coo_scaley does the same for the y axis.
Usage
coo_scale(coo, scale)
# Default S3 method
coo_scale(coo, scale = coo_centsize(coo))
# S3 method for class 'Coo'
coo_scale(coo, scale)
coo_scalex(coo, scale = 1)
# Default S3 method
coo_scalex(coo, scale = 1)
# S3 method for class 'Coo'
coo_scalex(coo, scale = 1)
coo_scaley(coo, scale = 1)
# Default S3 method
coo_scaley(coo, scale = 1)
# S3 method for class 'Coo'
coo_scaley(coo, scale = 1)Arguments
- coo
matrixof(x; y)coordinates or any Coo object.- scale
the scaling factor, by default, the centroid size for
coo_scale; 1 forscalexandscaley.
See also
Other coo_ utilities:
coo_align(),
coo_aligncalliper(),
coo_alignminradius(),
coo_alignxax(),
coo_baseline(),
coo_bookstein(),
coo_boundingbox(),
coo_calliper(),
coo_centdist(),
coo_center(),
coo_centpos(),
coo_close(),
coo_down(),
coo_dxy(),
coo_extract(),
coo_flipx(),
coo_force2close(),
coo_interpolate(),
coo_is_closed(),
coo_jitter(),
coo_left(),
coo_likely_clockwise(),
coo_nb(),
coo_perim(),
coo_range(),
coo_rev(),
coo_right(),
coo_rotate(),
coo_rotatecenter(),
coo_sample(),
coo_sample_prop(),
coo_samplerr(),
coo_shearx(),
coo_slice(),
coo_slide(),
coo_slidedirection(),
coo_slidegap(),
coo_smooth(),
coo_smoothcurve(),
coo_template(),
coo_trans(),
coo_trim(),
coo_trimbottom(),
coo_trimtop(),
coo_untiltx(),
coo_up(),
is_equallyspacedradii()
Other scaling functions:
coo_template()
Examples
# on a single shape
b <- bot[1] %>% coo_center %>% coo_scale
coo_plot(b, lwd=2)
coo_draw(coo_scalex(b, 1.5), bor="blue")
coo_draw(coo_scaley(b, 0.5), bor="red")
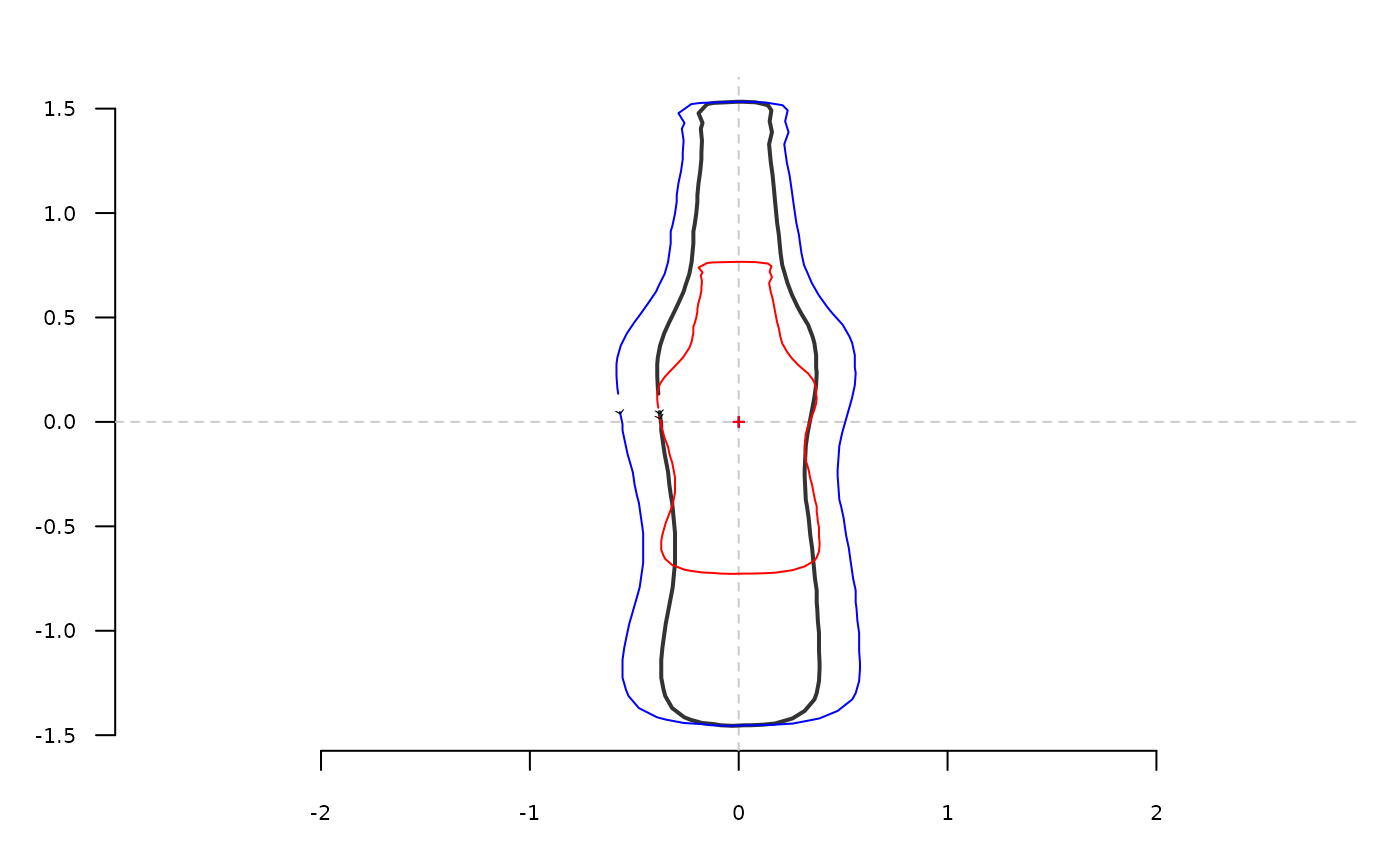 # this also works on Coo objects:
b <- slice(bot, 5) # for speed sake
stack(b)
# this also works on Coo objects:
b <- slice(bot, 5) # for speed sake
stack(b)
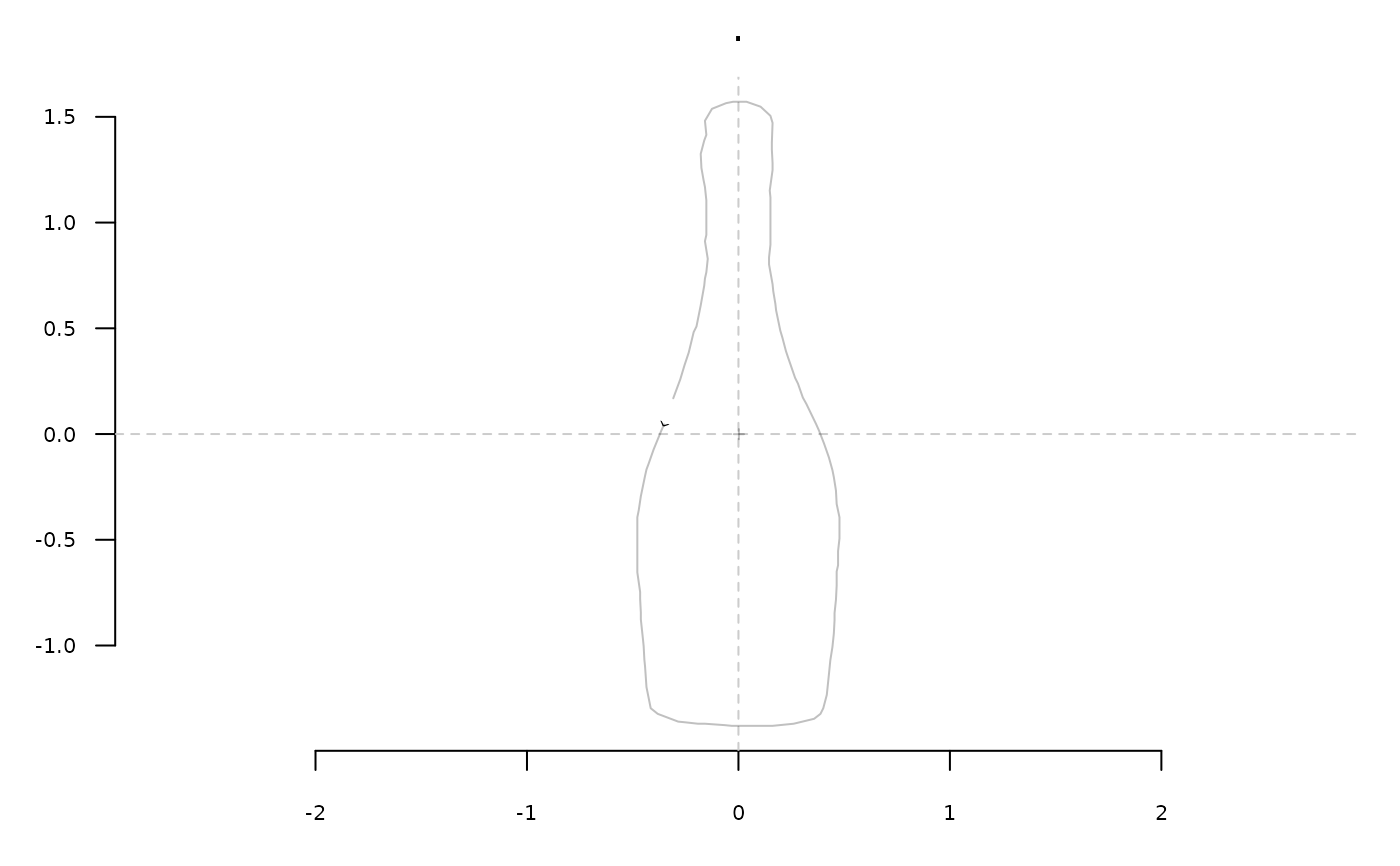
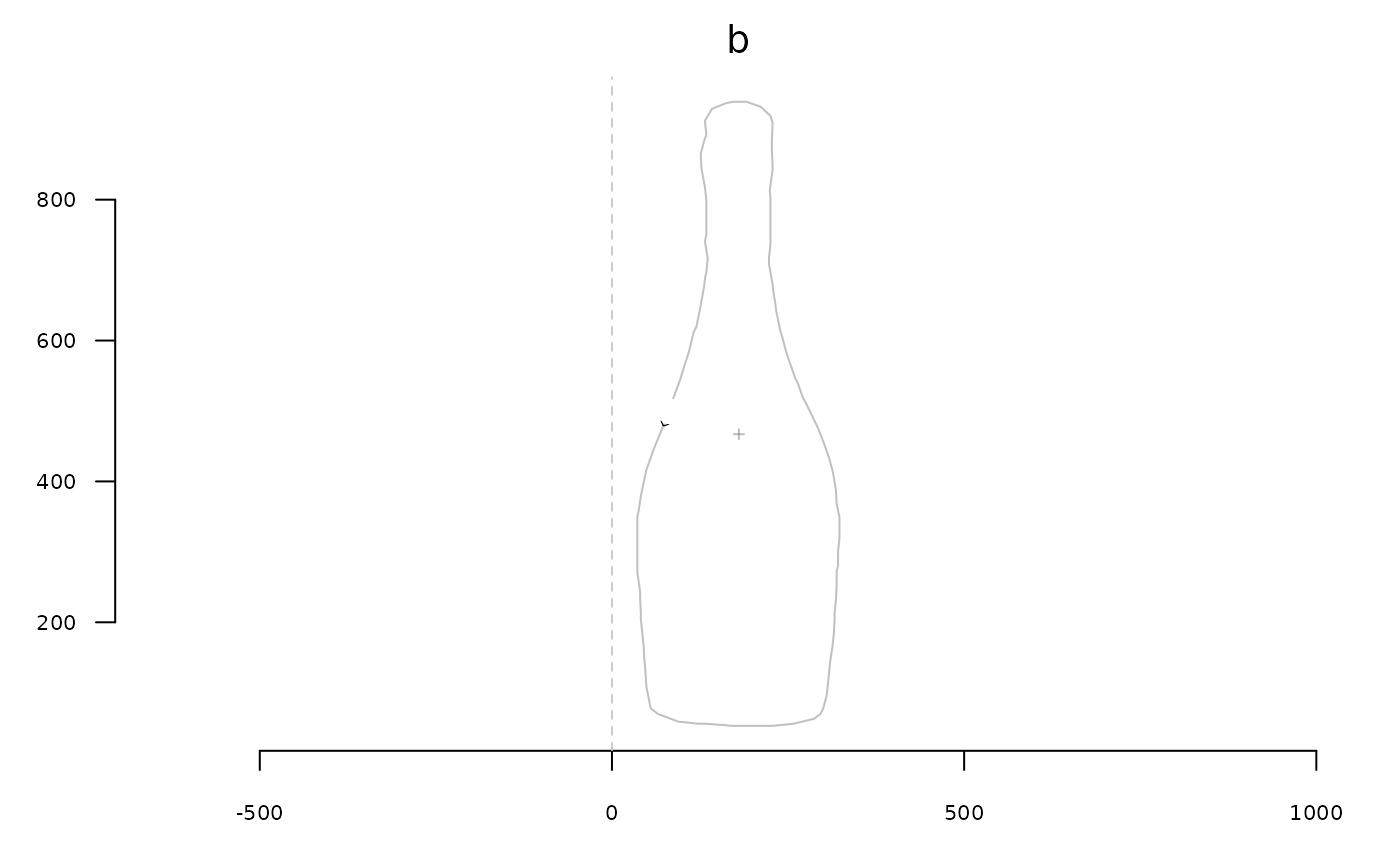 b %>% coo_center %>% coo_scale %>% stack
b %>% coo_center %>% coo_scale %>% stack
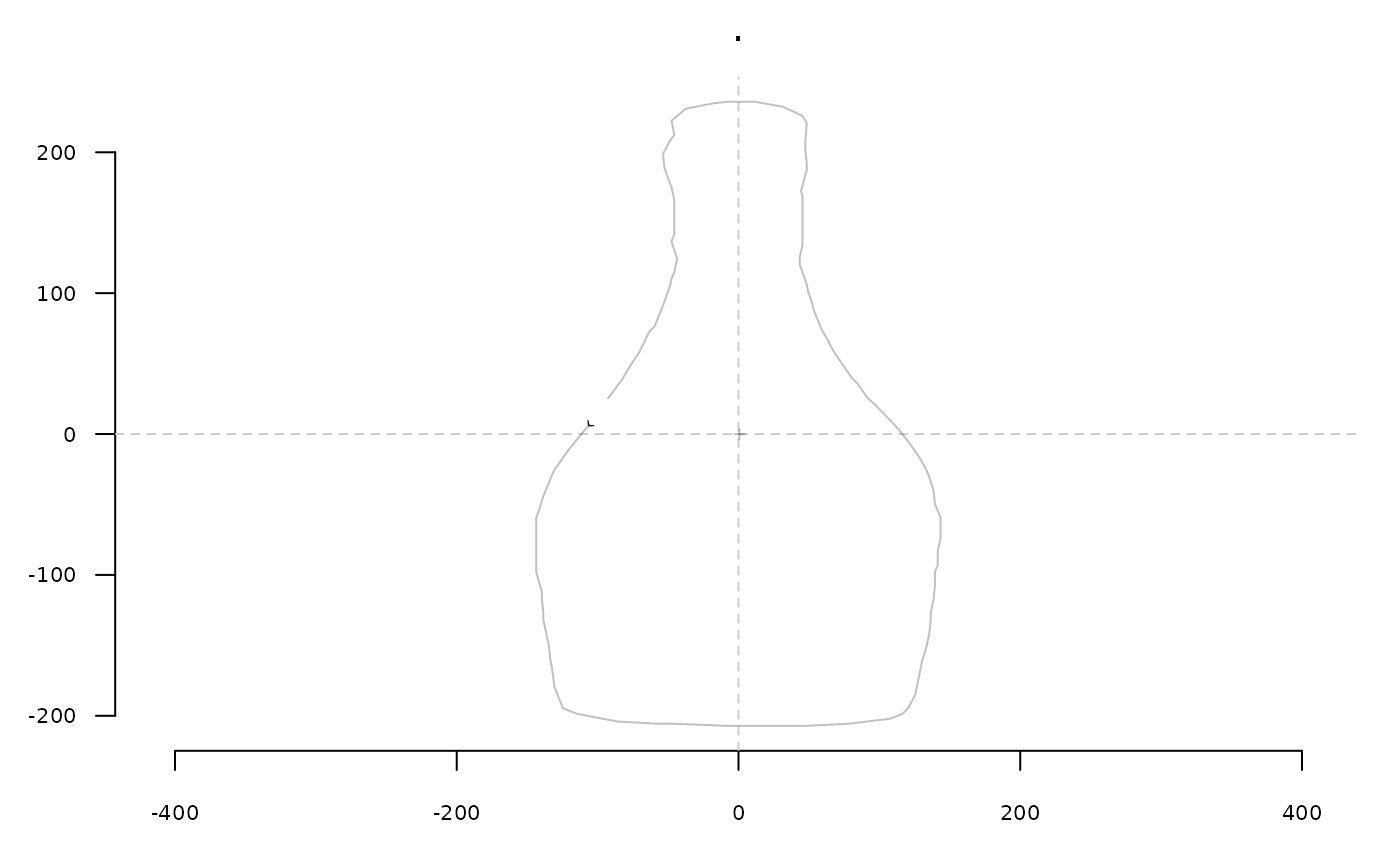
 b %>% coo_center %>% coo_scaley(0.5) %>% stack
b %>% coo_center %>% coo_scaley(0.5) %>% stack
 #equivalent to:
#b %>% coo_center %>% coo_scalex(2) %>% stack
#equivalent to:
#b %>% coo_center %>% coo_scalex(2) %>% stack
